Pharma Polymers
How medicine reliably reaches its target
How liposomes play a key role in cancer therapy by transporting ribonucleic acids to the affected cells.

Pharma Polymers
Transport without Side Effects
Drug delivery—on the art of transporting active pharmaceutical ingredients to specific targets in the human body.

Pharma Polymers
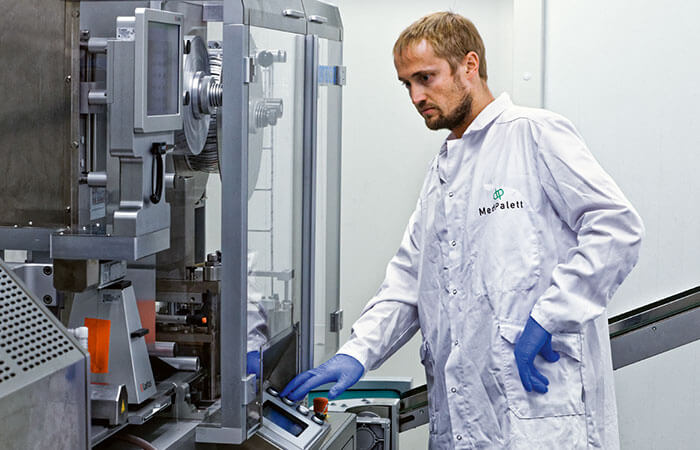
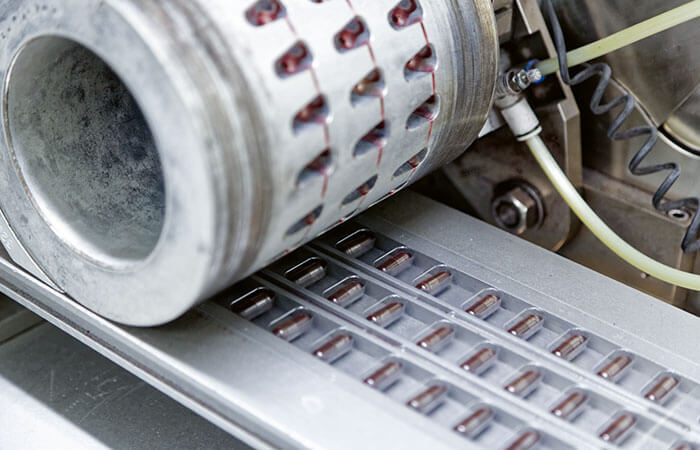
How Medications Enter the Body
The “chemical packaging” and the navigation to specific targets are becoming ever more precise.

Research
Protecting the Skin
Our skin protects us from environmental effects. But what protects our skin? New active ingredients that promote detoxification, for example.
ELEMENTS Newsletter
Get fascinating insights into the research Evonik is conducting, and its social relevance, by subscribing to our free newsletter.